Ceteris Paribus Meaning in Economics
Ceteris paribus Economists often simplify analysis by setting aside things that are thought to be of less importance to the question of interest. Ceteris Paribus Assumption - means all other things held constant or all else equal This assumption is used as a device to analyze the relationship between two.
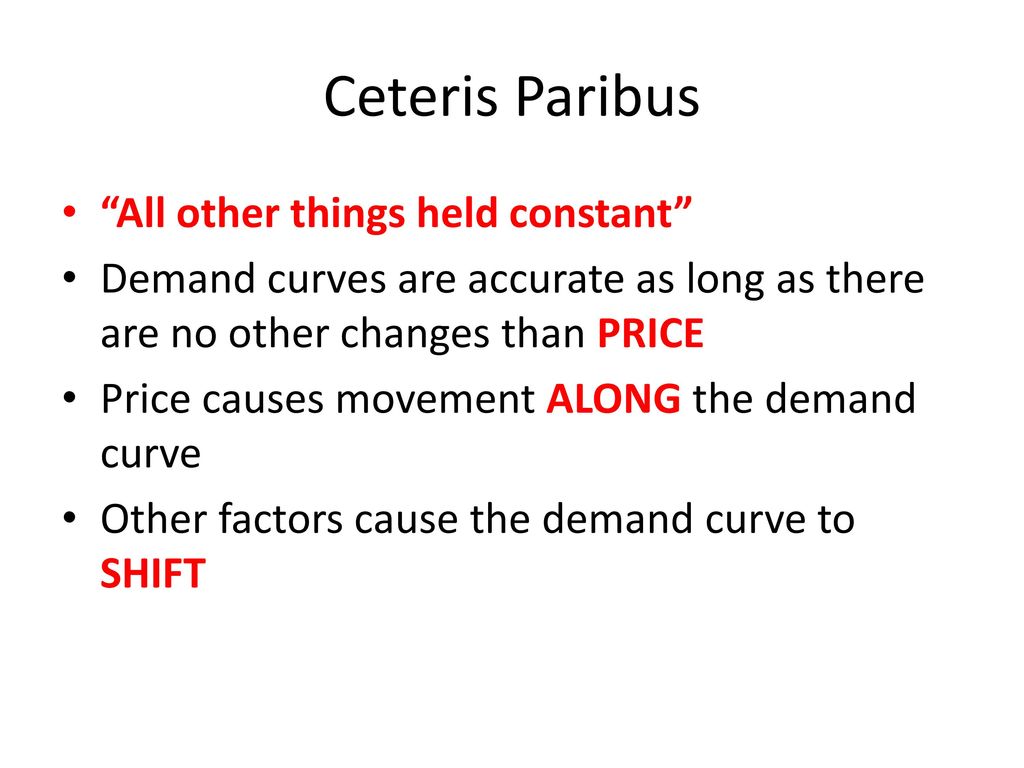
Ceteris Paribus All Other Things Held Constant Ppt Download
In an economic model it means an analysis holds other things constant.

. This presents the different prices of a good and the corresponding quantity demanded per unit of time. Estimation of such effects has been a primary focus of empirical economics from the earliest years of econometrics Disciplines lacking natural models invented new oneseg the PO. This was the lesson I had to learn in three years spent in Auschwitz and Dachau.
The literal meaning of the expression is other things equal. Ceteris paribus a Latin phrase meaning all else being equal helps isolate multiple independent variables affecting a dependent variable. Ceteris paribus is a Latin phrase meaning all other things remaining equal.
Definition of ceteris paribus. For example the price of a particular good might be fixed at 10 per unit for a year. What Does Ceteris Paribus Mean.
At a price of 4 per pound for example producers are willing to supply 15 million pounds of coffee per month. This concept central to economics since Alfred Marshall. It describes the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Alfred Marshall defined the Law thus. Nominal rigidity also known as price-stickiness or wage-stickiness is a situation in which a nominal price is resistant to change. In year 2 if the output stays at 1000 units but money supply increases to 15000.
There is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded ceteris paribus. The process of collecting sample observations from a larger population over a given time period. A higher price say 6 per pound induces sellers to supply.
Therefore firms put up prices to reflect this increase in money supply. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Consumers have more money to buy the same amount of goods.
I Demand Schedule and Demand Curve. Figure 38 A Supply Schedule and a Supply Curve gives a supply schedule for the quantities of coffee that will be supplied per month at various prices ceteris paribus. Complete nominal rigidity occurs when a price is fixed in nominal terms for a relevant period of time.
Second nature to economists. Enter the email address you signed up with and well email you a reset link. The term management of household pertains to the microeconomic branch of economics while state management refers to the macroeconomic branch of economics.
Ceteris paribus other things being equal those most apt to survive the camps were those oriented toward the futuretoward a task or a person waiting for them in the future toward a meaning to be fulfilled by them in the future Frankl 1978 p. The concept of ceteris paribus is important in economics because in the real world it is usually hard to isolate all the different variables. Acausal effectis just the responses to ceteris paribus changes taught in Econ101 everywhere.
Incentive Economic reward or punishment which influences the benefits and costs of alternative. Longitudinal data is used in statistical and financial studies. Assuming ceteris paribus allows us to simplify economics we can understand how something like higher price will affect demand.
Microeconomics is a field which analyzes whats viewed as basic elements in the economy including individual agents and. Ceteris paribus average prices. Economics ˌ ɛ k ə ˈ n ɒ m ɪ k s ˌ iː k ə- is the social science that studies the production distribution and consumption of goods and services.

Economics 214 Lecture 18 Ceteris Paribus Economic Analysis Often Proceeds By Considering The Consequences Of A Certain Event Ceteris Paribus The Advantage Ppt Download



No comments for "Ceteris Paribus Meaning in Economics"
Post a Comment